The Seattle metropolitan area’s ambitious light rail expansion represents one of the most complex and expensive transit projects in U.S. history, facing significant construction challenges while fundamentally reshaping regional development patterns and work commute behaviors. It is also turning Seattle into an attraction for those working at home who are more and more being required to visit an employer office a few times a week.

Background
Work-from-home patterns directly explain downtown vacancy challenges. Seattle’s office vacancy rate reached 26.1% in Q2 2025, with downtown Seattle hitting 33%. The target vacancy rate is 10%. The timing correlation is unmistakable: areas with the highest remote work adoption show the steepest commercial real estate declines.
Tourism-focused cities appear to draw businesses away from less prominent locations, such as Bellevue Washington. Companies relocating to tourested downtowns, like Seattle, cite access to clients, networking opportunities, and brand-building advantages that suburban locations cannot provide. The concentration of resources in major tourism destinations creates a challenging environment for smaller downtowns competing for the same businesses and shoppers.
The data suggests a clear hierarchy: major tourism destinations like San Francisco, Los Angeles and now Seattle continue attracting downtown investment despite challenges, while secondary cities like Portland and suburbs like Bellevue struggle more significantly. Smaller suburban downtowns face the steepest challenges, lacking both the tourism draw of major cities and the housing cost advantages that once made suburban locations attractive. Regional Transportation systems like light rail disadvantage the downtowns that lack major attractions. What follows is a brief history of the Seattle metropolitan area light rail that is useful in explaining the current area situation. It should be of interest to anyone planning to live or otherwise invest in the area.
Major Construction Challenges
Seattle’s light rail system has confronted numerous obstacles that have dramatically increased costs and delayed timelines. Sound Transit currently faces a staggering $20-30 billion shortfall in its long-term budget, representing approximately 25% of the entire ST3 expansion program. This massive gap stems from multiple factors including inflation, pandemic-related delays, concrete worker strikes, collapsed embankments, and persistent quality control issues with track supports. constructiondive+2
The East Link extension to Bellevue and Redmond alone has experienced particularly severe problems since 2019, when inspectors discovered that concrete plinths failed to properly connect with rails. The contractor, Kiewit-Hoffman joint venture, installed mortar between blocks and rails, but this solution also failed, leading to additional concrete placement issues. These problems have resulted in delays of at least a year for the most complex 14-mile segment, which involves the world’s first effort to build and operate rail across a floating bridge.constructiondive
The Bertha Tunnel Boring Machine Controversy
One of the most significant infrastructure challenges involved the massive tunnel boring machine “Bertha,” used for the SR-99 viaduct replacement tunnel project. In December 2013, Bertha stalled after encountering an 8-inch diameter steel pipe left from a 2002 groundwater monitoring well. This incident triggered a complex legal battle over responsibility and costs.wikipedia

The contractor Seattle Tunnel Partners (STP) was ultimately held liable for the delays and damages. In 2019, a jury ordered STP to pay Washington State $57 million in penalties for the 867-day delay. The state successfully argued that STP had knowledge of the pipe’s location prior to excavation, despite the contractor’s claims that the pipe constituted an unforeseen site condition. Additionally, the Washington Supreme Court ruled in 2022 that insurers were not required to pay for tunnel delays because the damage was considered poor management rather than a physical business risk. seattletimes+2

Underground Infrastructure and Tunnel Network
Seattle’s light rail system includes extensive underground sections totaling approximately 10-12 miles of tunnels:
Downtown Seattle Transit Tunnel (DSTT): 1.3 miles serving four stations (Westlake, University Street/Symphony, Pioneer Square, International District/Chinatown)wikipedia The Downtown Seattle Transit Tunnel was used exclusively by hybrid articulated buses—specifically Breda dual-mode buses that switched from diesel to electric power in the tunnel—from its opening on September 15, 1990, until bus service ended on March 23, 2019. This

- University Link Tunnel: 3.15 miles connecting downtown to University of Washington via Capitol Hill, reaching depths of 300 feet below groundwikipedia This tunnel goes under the Montlake Cut which means it goes under water.

- Northgate Link Tunnel: 3.5 miles of twin tunnels extending from University of Washington to Northgatesoundtransit

- Beacon Hill Tunnel: Approximately 1 mile through Beacon Hilltrainorders
- Downtown Bellevue Tunnel: 2,000 feet for the East Link extensionsoundtransit The transformation of Lake Washington’s eastern shore from a blue-collar industrial region centered around shipbuilding to one of America’s wealthiest white-collar enclaves represents one of the most dramatic economic metamorphoses in U.S. urban history. This shift, spanning roughly 80 years from the 1940s has significant implications for light rail.
The underground portions of the metropolitan light rail system in Seattle are of particular interest to engineers and architects as well as those interested in public artworks.
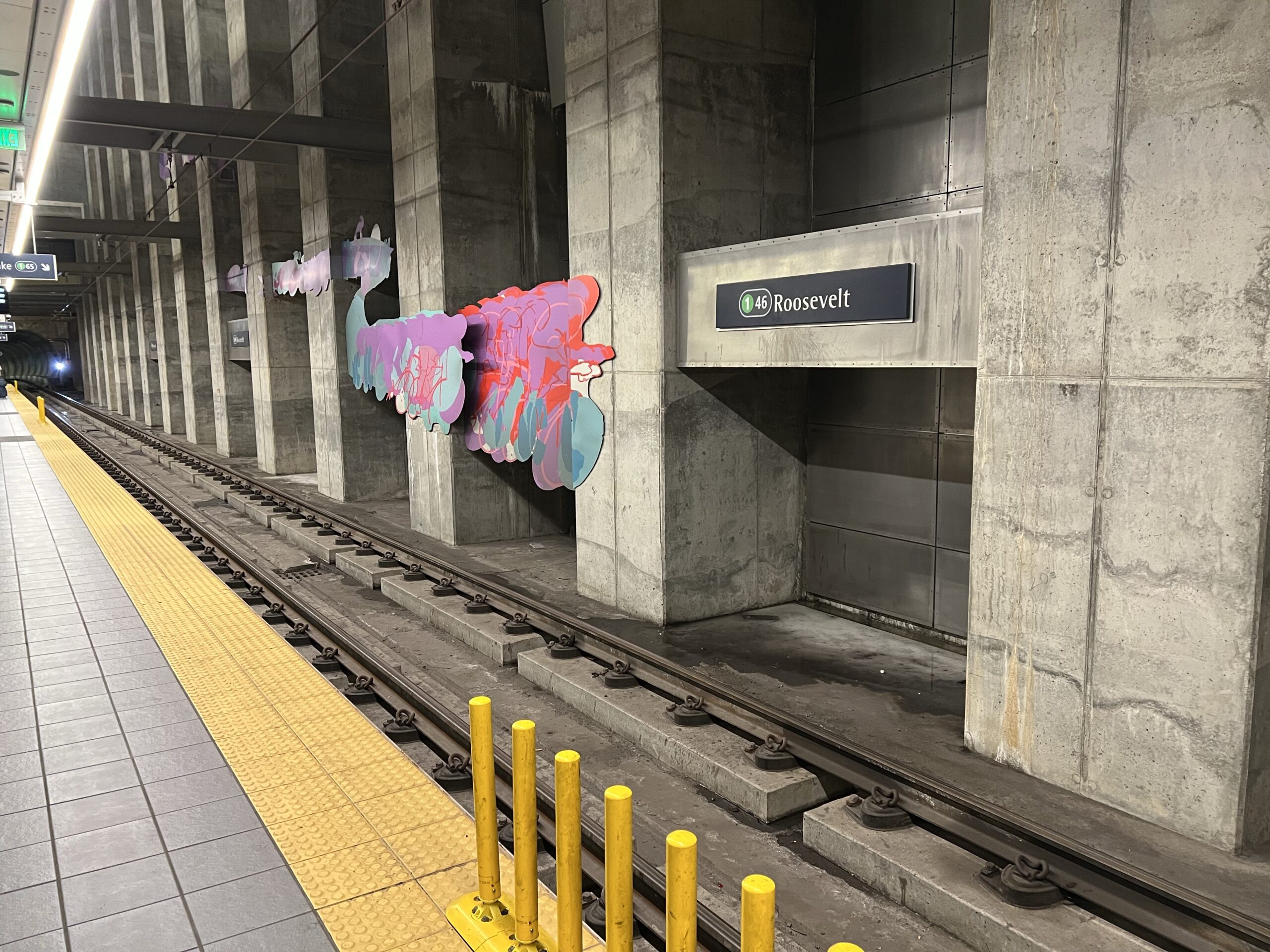
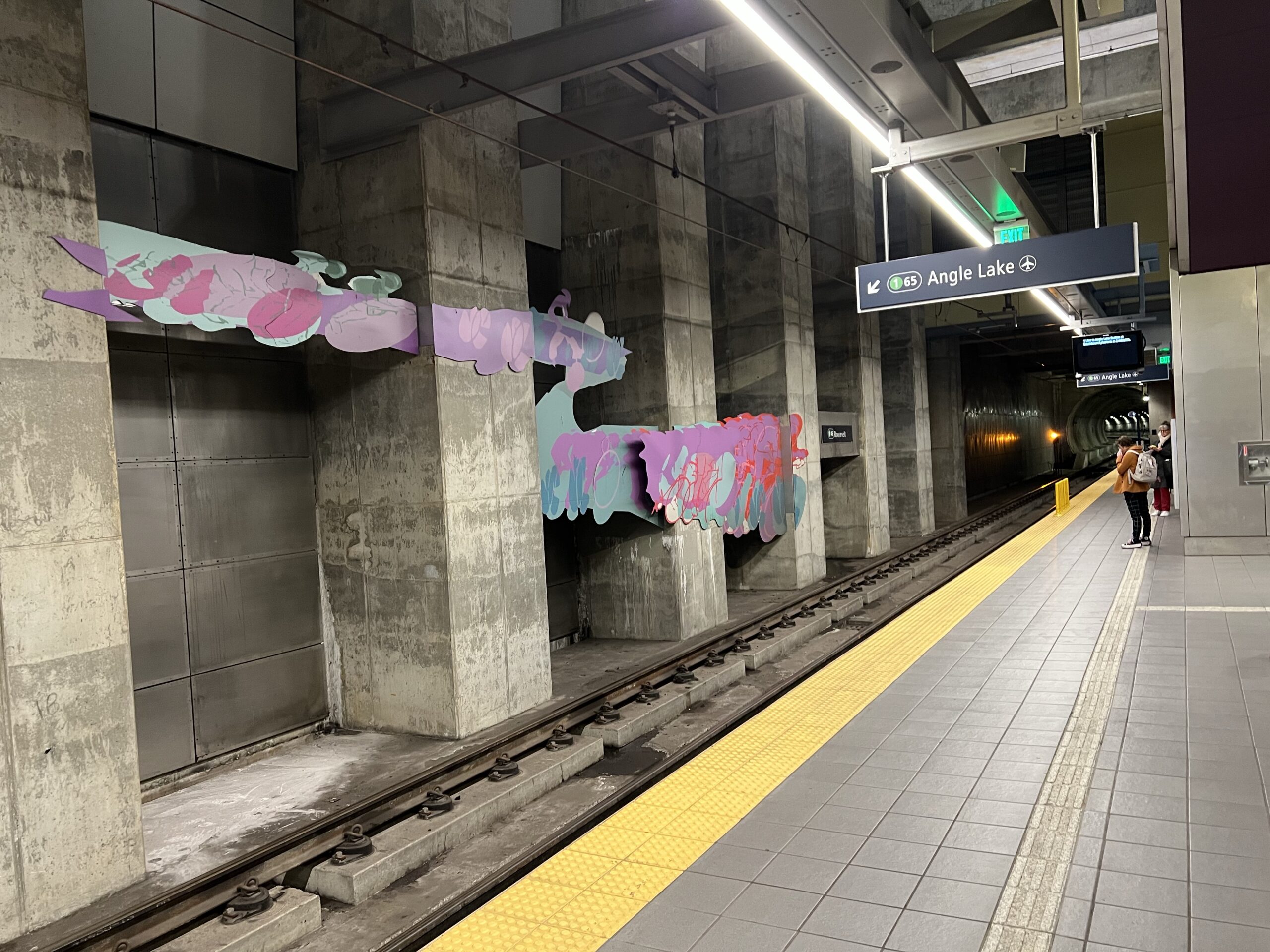
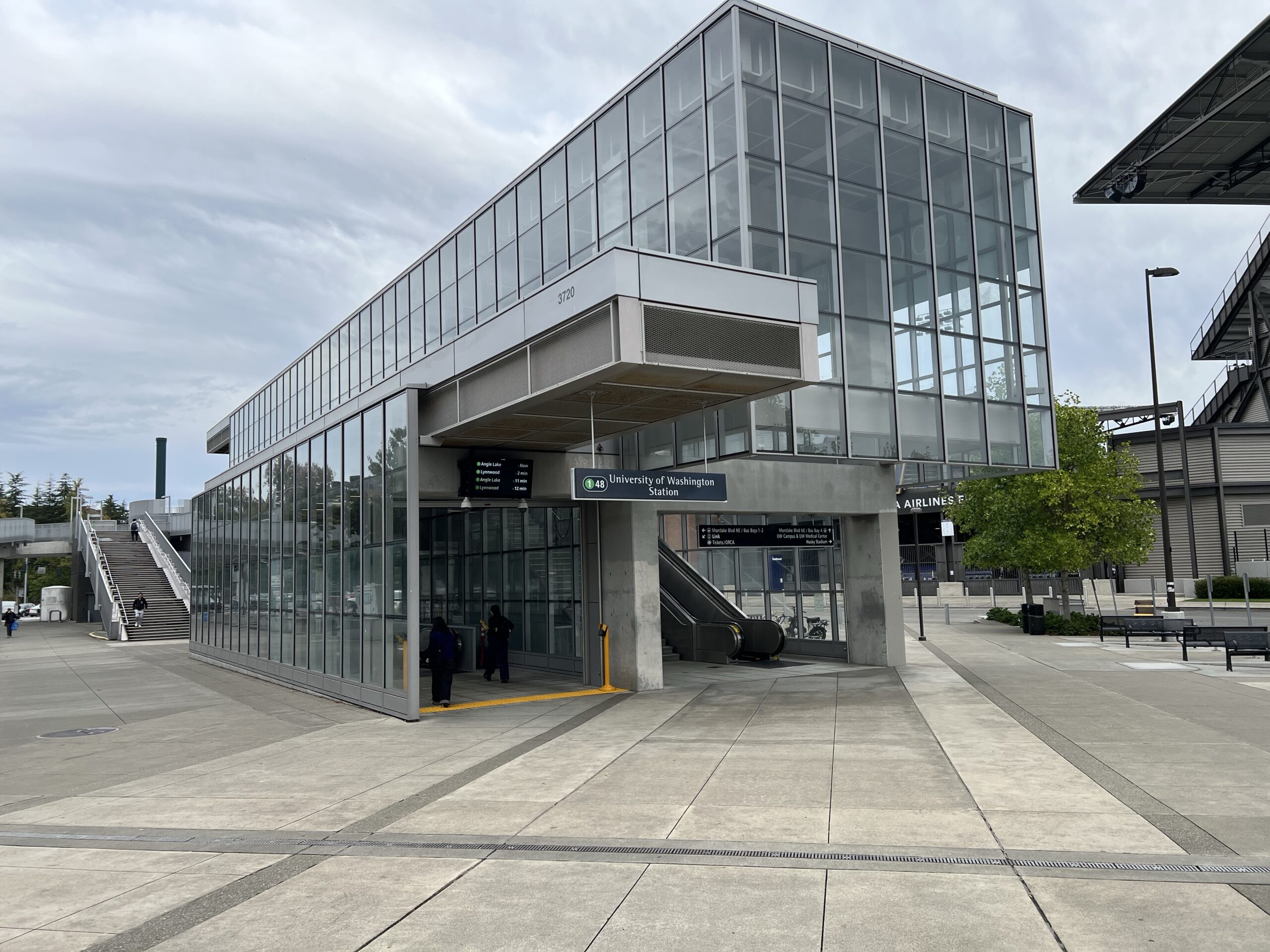
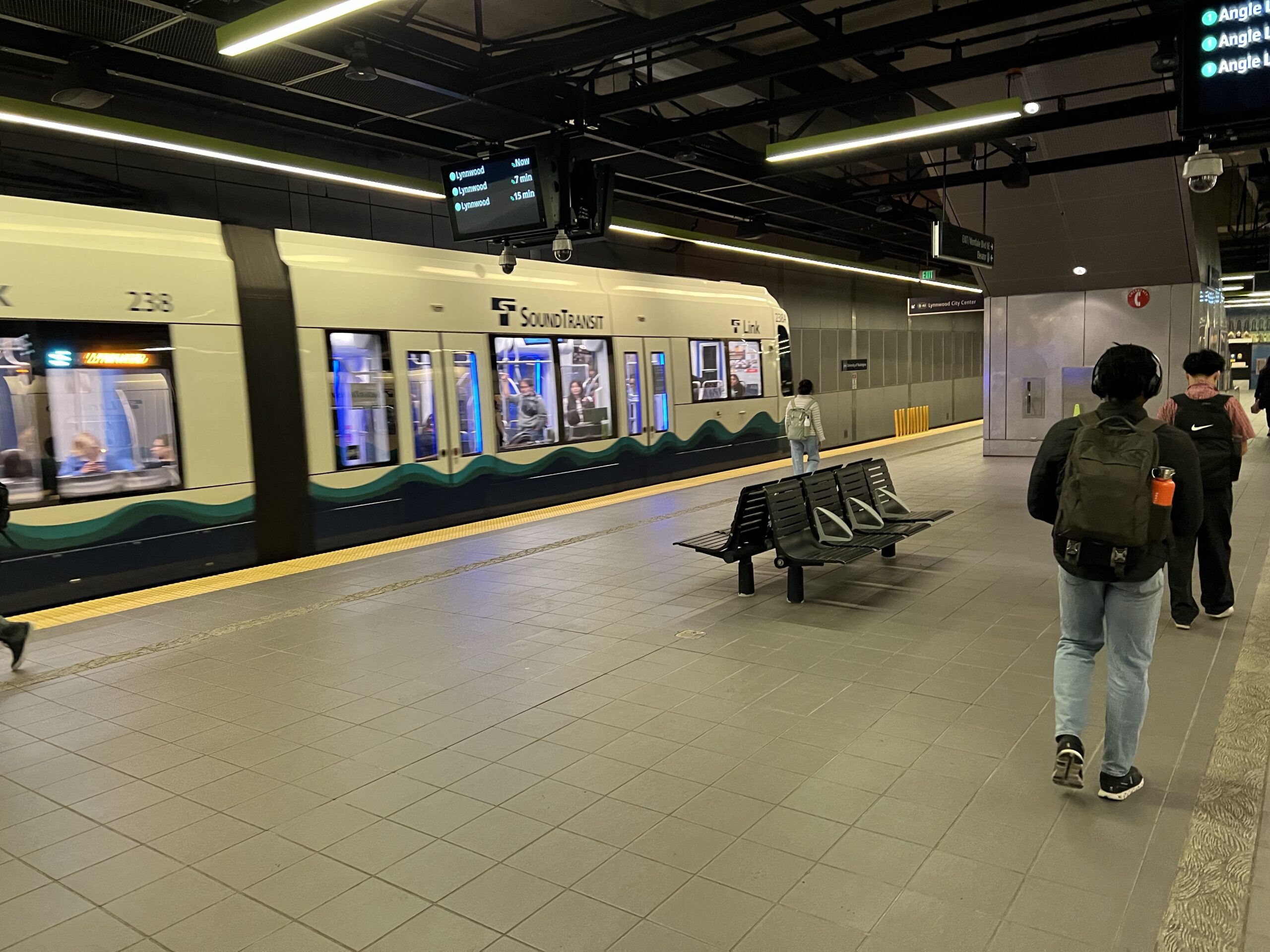

















The Office Disneyland
As mentioned previously, Seattle’s office vacancy rate is near its highest ever. Bellevue’s vacancy rate is significantly worse. This is confusing when compared with lease rates where Bellevue betters Seattle and is explained partly by Microsoft’s recent retreat from Bellevue to an expanded campus in Redmond. It is also explained by Amazon’s slower-than-expected occupancy of the space they have leased in Bellevue. Amazon still has around 40% of its Bellevue square footage unoccupied heading into fall 2025.

It should be noted that many believe the leasing of unused space in Bellevue is related to Seattle tax policy. Seattle does not currently have a general per employee head tax; a prior “head tax” on large employers like Amazon was enacted in 2018 but repealed within weeks after significant opposition from Amazon and other businesses. In 2025, Seattle implemented a new payroll tax on excess compensation above $1 million per employee, designed to fund affordable housing, but this is different from a per-employee head tax.[1][2][3][4][5]

Amazon’s extensive leasing of about a dozen office buildings in Bellevue officially is primarily driven by its growth plans and consolidation of regional offices rather than specifically to avoid a Seattle tax. While corporate tax initiatives in Seattle may have influenced Amazon’s expansion strategy, the repeal of Seattle’s original head tax in 2018 was a significant factor in maintaining its Seattle presence. The new 2025 payroll tax on high earners is more targeted and has not caused Amazon to shift its entire footprint out of Seattle, but it adds costs to employers with highly paid employees in the city.[2][3][4][6][7][8][1]
In summary:
- Seattle repealed its original per employee head tax in 2018 after opposition led by Amazon.
- Amazon leases many Bellevue offices officially due to growth needs, with some political factors influencing location choices.
- The 2025 Seattle payroll tax on excess compensation is a new tax but not a general head tax that is not objectionable to Amazon
This indicates Seattle’s back off on a broad head tax was indeed influenced by Amazon’s opposition. The repeal of Seattle’s head tax was widely seen as influenced by Amazon’s lobbying and political pressure.
If Amazon’s leasing of about a dozen office buildings in Bellevue is primarily related to its regional growth and consolidation plans rather than specifically to avoid Seattle’s taxation, then its management miscalculated.
The median home price in Bellevue is extremely high, around $1.45 million to $1.7 million in early to mid-2025, reflecting strong price appreciation and a tight market. Unless Bellevue can build affordable apartments, there is little hope of filling Amazon leased offices. Light rail stations in Bellevue are not likely to be popular with riders who don’t live in the city and Amazon employees are not likely to move there. At least for the next decade, transit cannot help Bellevue with its downtown situation. In fact, baring heavy lobbying, the Bellevue rail stations are likely to be the last constructed given the 20 to 30 billion cost shortfall and low ridership expected from there.
Sources
[1] Prepare for Seattle’s New Excess Compensation Payroll Tax https://www.mossadams.com/articles/2025/03/seattle-excess-compensation-payroll-tax
[2] Amazon Backlash Spurs Seattle City Council to Repeal ‘Head Tax … https://www.governing.com/archive/tns-seattle-head-tax-repeal.html
[3] Seattle adopts tax on certain compensation exceeding $1 million: PwC https://www.pwc.com/us/en/services/tax/library/pwc-seattle-adopts-tax-on-certain-compensation-exceeding-1-million.html
[4] Seattle Repeals Tax On Big Business After Opposition From … – NPR https://www.npr.org/2018/06/13/619444956/seattle-repeals-tax-on-big-business-after-opposition-from-amazon-starbucks
[5] Amazon won a major battle in Seattle, but a Big Tech ‘head tax … https://finance.yahoo.com/news/amazon-won-major-battle-seattle-141500116.html
[6] Amazon Reportedly Leases Space at WeWork in Bellevue https://downtownbellevue.com/2020/04/20/amazon-reportedly-leases-space-wework-bellevue/
[7] Amazon leases another Bellevue office tower as it makes room for … https://www.geekwire.com/2021/amazon-leases-another-bellevue-office-tower-makes-room-planned-25k-employees-city/
[8] Amazon’s commitment to Bellevue and the Eastside https://www.aboutamazon.com/news/job-creation-and-investment/amazons-commitment-to-bellevue-and-the-eastside
[9] r/SeattleWA – Amazon leases another Bellevue office tower as it … https://www.reddit.com/r/SeattleWA/comments/m1mgmk/amazon_leases_another_bellevue_office_tower_as_it/
[10] A look at the planned Summit III building in downtown Bellevue that … https://getthewreport.com/the-state-of-real-estate/a-look-at-the-planned-summit-iii-building-in-downtown-bellevue-that-amazon-is-taking-lmn-architects-rendering/
[11] Payroll expense tax – City Finance | seattle.gov https://www.seattle.gov/city-finance/business-taxes-and-licenses/seattle-taxes/payroll-expense-tax
[12] How Amazon Helped Kill Seattle a Tax On Business – The Atlantic https://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2018/06/how-amazon-helped-kill-a-seattle-tax-on-business/562736/
[13] Seattle voters approve payroll expense tax on high earners – RSM US https://rsmus.com/insights/tax-alerts/2025/seattle-voters-approve-payroll-expense-tax-on-high-earners.html
[14] Not just an ‘Amazon tax’: Other Seattle businesses join head-tax fight https://www.seattletimes.com/business/wide-range-of-seattle-businesses-speak-out-against-head-tax-proposal/
[15] Bold or boneheaded? Seattle’s proposed tax hike on big … – GeekWire https://www.geekwire.com/2025/boneheaded-or-bold-seattles-new-tax-proposal-on-big-businesses-sparks-debate/
[16] Amazon Is Wrong on the Head Tax – Seattle – The Urbanist https://www.theurbanist.org/2018/05/12/amazon-wrong-head-tax/
[17] Seattle’s head tax: Look carefully at who’s behind it https://www.freedomfoundation.com/labor/seattles-head-tax-look-carefully-at-whos-behind-it/
[18] Amazon signs new lease for 25-story Bellevue tower https://www.seattletimes.com/business/amazon/amazon-signs-new-lease-for-25-story-bellevue-tower/
[19] The Seattle Payroll Expense Tax – What You Need to Know https://clarknuber.com/articles/seattle-payroll-tax-explained-what-employers-need-to-know/
[20] Bellevue real estate brokers bullish about Amazon’s new return-to … https://www.geekwire.com/2024/the-lift-that-we-need-bellevue-real-estate-brokers-bullish-about-amazons-new-in-office-policy/
This bleak short term situation doesn’t mean all is lost. Bellevue Realtors point to successful office concepts where the office is its own attraction. This is known as the office Disneyland.
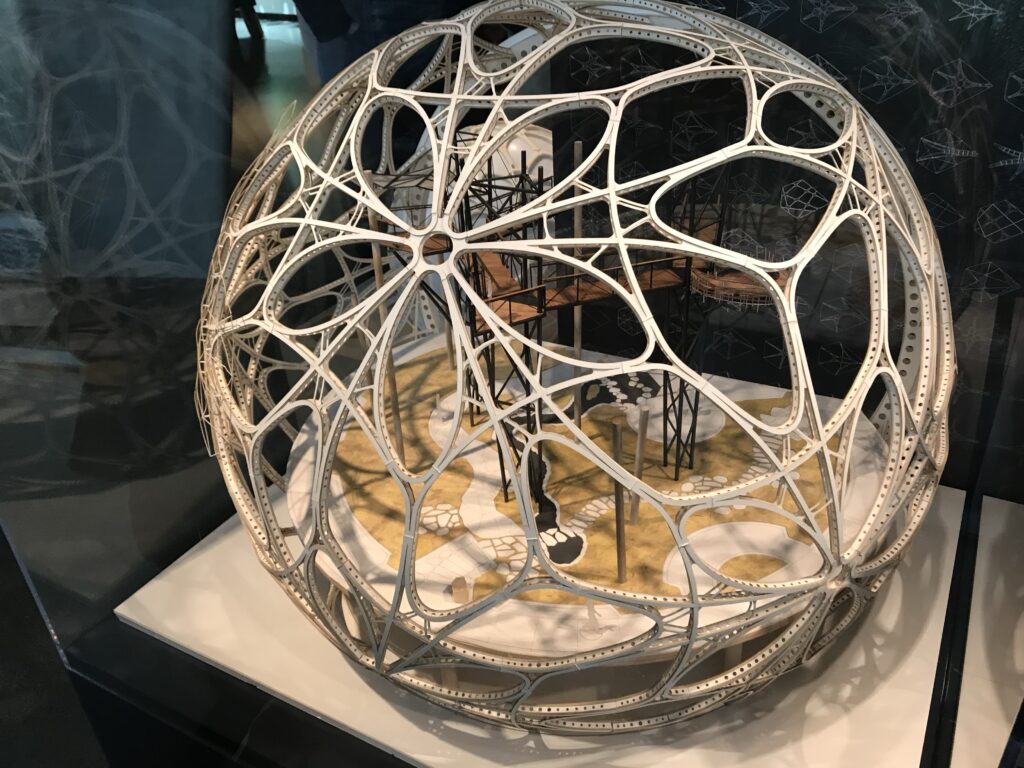

“Disneyland” Features in Bellevue Office Buildings include the New Bellevue office towers, like Amazon’s Sonic tower and the 555 Tower, are adding lifestyle and entertainment amenities that blur the boundaries between work and leisure. These features include:
• Sky lounges and communal spaces with sweeping views
• Indoor plantings and horticultural elements inspired by Amazon’s “The Spheres” in Seattle
• Flexible breakout spaces, coffee bars, bistros, and social zones
• Entertainment facilities such as bocce courts, bowling, and high-end restaurants
• Wellness amenities, bike lockers, state-of-the-art fitness centers, and outdoor terraces
The goal is to create workplaces as attractive, engaging, and comfortable as home (or even more so), hoping that experience-focused amenities—not just workstations—will draw hybrid and remote workers from outside of the city into the downtown office.
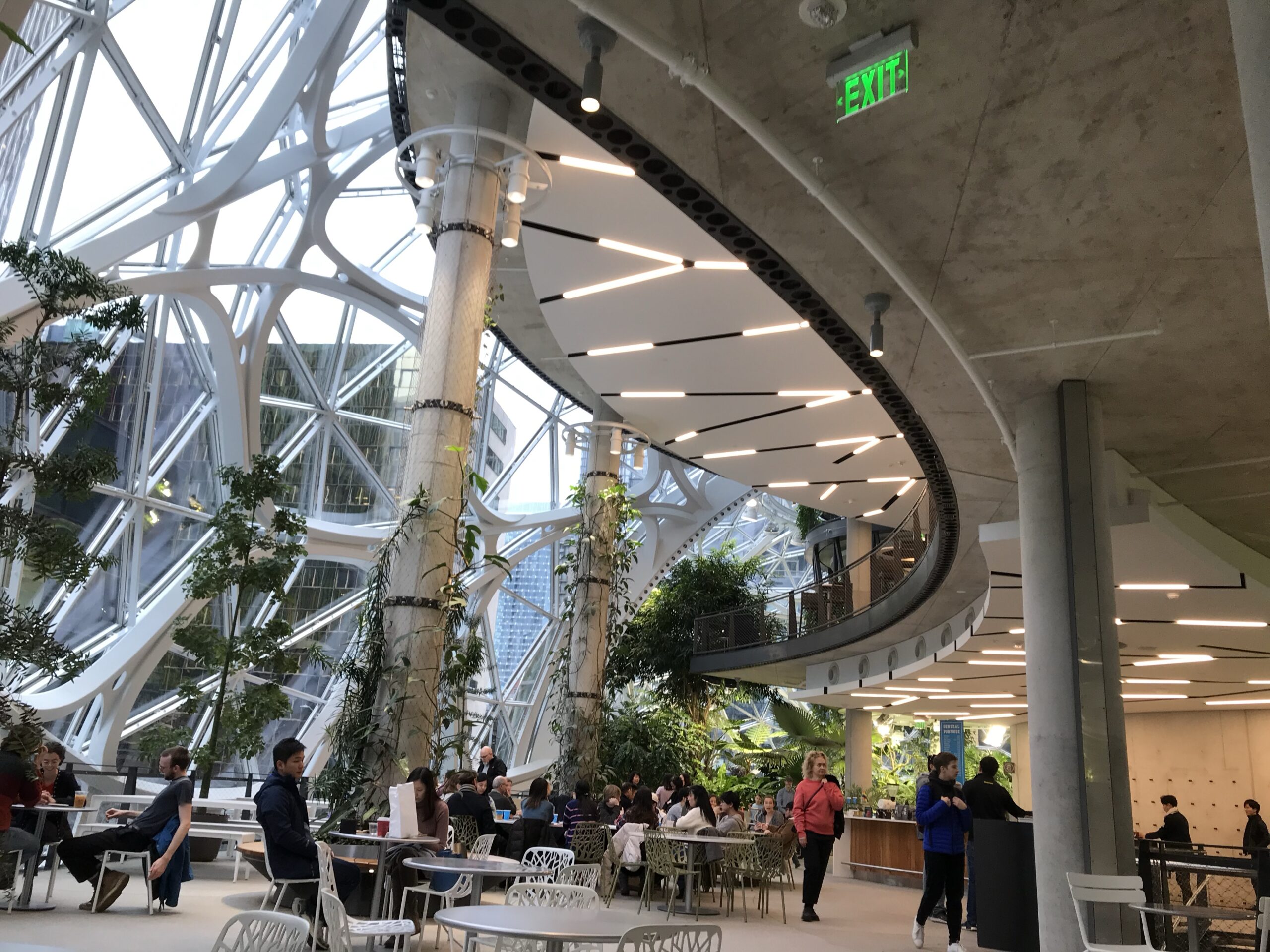
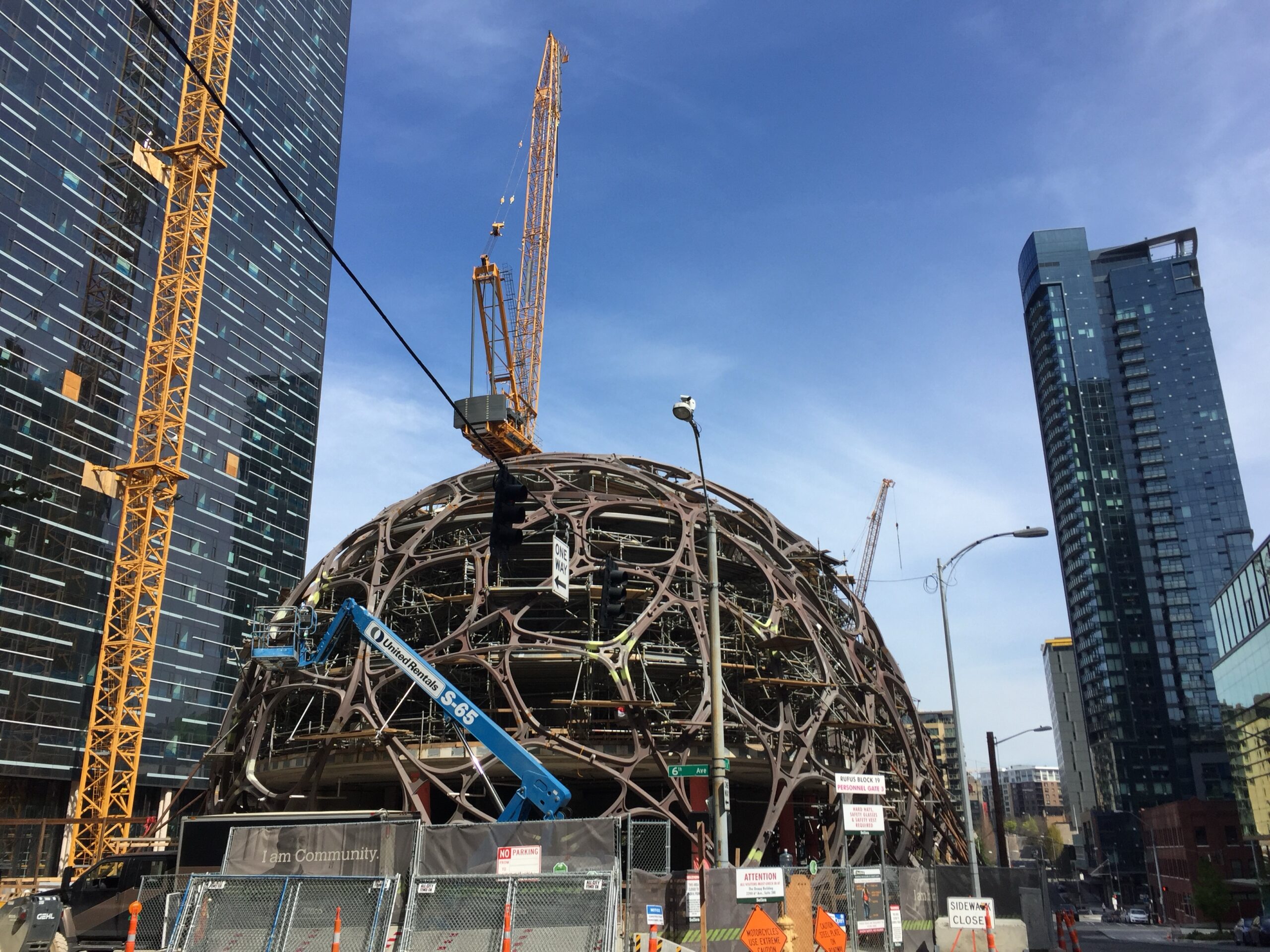
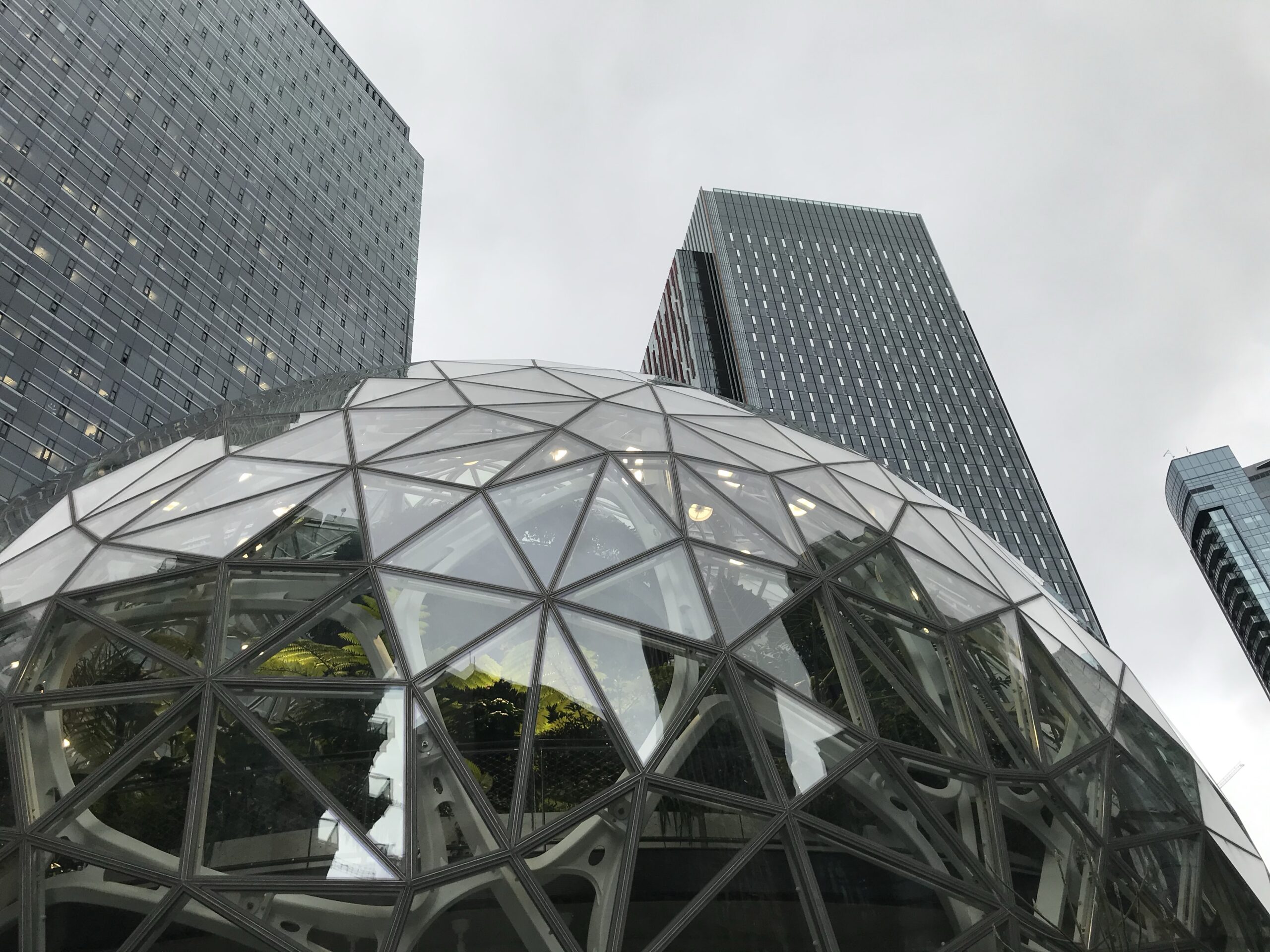







Overall, Bellevue and Seattle are seeing high office vacancies as remote and hybrid work continue to dominate, with landlords relying on entertainment, wellness, and social features to recast the office as a destination rather than an obligation for those workers.
FIFA World Cup 2026 Readiness
Seattle’s light rail system is strategically positioned to support the FIFA World Cup 2026, with several key developments:
Available Infrastructure by 2026:
- The existing 1 Line serving downtown Seattle to Lynnwood and south to Angle Lake is fully operationalyoutube
- The East Link extension connecting Seattle to Bellevue and Redmond is expected to open in early 2026, adding 14 miles and 10 stationsyoutube
- Enhanced service frequencies and extended operating hours during tournament periodsseattleelitetowncar

Operational Preparations:
Sound Transit has been studying transit management strategies from cities like Paris and Doha that recently hosted major events. The agency plans to deploy additional staff, security, and transit ambassadors at key stations, particularly those near Lumen Field including International District/Chinatown, Pioneer Square, Westlake, and SeaTac Airport. New multilingual signage with walking distance markers in both miles and kilometers is being tested for international visitors.youtube
Transit-Oriented Development Impact
Light rail stations have catalyzed significant development activity throughout the region, fundamentally altering land use patterns and property values near transit nodes.
Development Statistics:
- Sound Transit has successfully implemented numerous transit-oriented development (TOD) projects, with over 232 affordable housing units completed or planned at Northgate Station alonekingcounty
- The Spring District Station TOD project will create 234 affordable homes in two buildings on land contributed by Sound Transit and the City of Bellevuesoundtransit
- Cedar Crossing at Roosevelt Station opened in 2022 with over 250 affordable homes, demonstrating successful integration of housing, childcare, and retail servicessoundtransit
Market Response:
The Roosevelt Station area exemplifies the transformative power of light rail access, experiencing rapid growth and development since the station opened. Property values have increased significantly in station areas, though Sound Transit’s policy requires that 80% of surplus property suitable for housing be offered to qualified entities for affordable housing development, with at least 80% of units affordable to families earning 80% or less of area median income.seattletimes+1
Remote Work and Downtown Office Visitation
The relationship between light rail and work-from-home patterns presents a complex dynamic that challenges traditional transit planning assumptions.
Developers in Bellevue are trying a range of hospitality and entertainment features—sometimes dubbed the “Disneyland” effect—to draw home-based workers back to the office. Seattle, already a major tourist attraction, sport and entertainment hub, has also implemented a Disneyland strategy.
Current Commute Trends:
Recent survey data reveals evolving work patterns as companies increasingly mandate return-to-office policies. Citywide, fully remote work decreased by 8% in 2024 compared to 2022, while transit use increased by 3% and drive-alone trips rose by 6% for downtown commuters. This represents the first upward trend in solo driving in a decade, suggesting that light rail alone cannot fully capture the returning workforce.downtownseattle+1
Hybrid Work Patterns:
Monday and Friday remain the most popular remote work days, with Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursday seeing the highest in-person office attendance. This concentrated mid-week presence creates peak demand periods that strain transit capacity while leaving systems underutilized on traditional “remote days.”downtownseattle
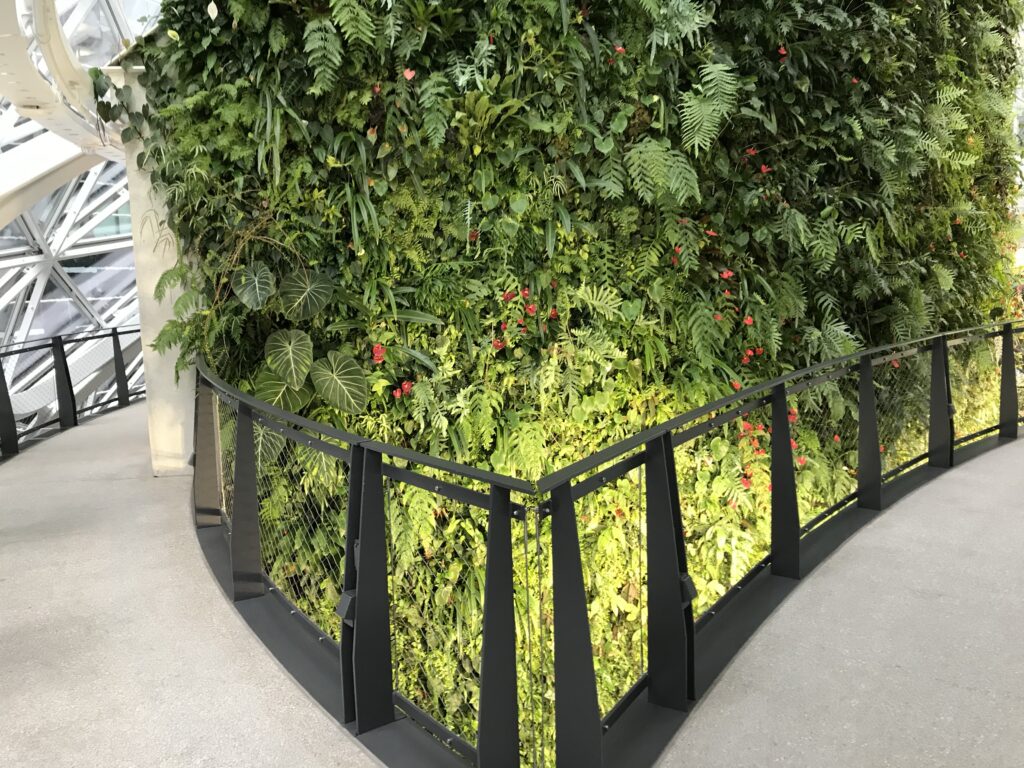
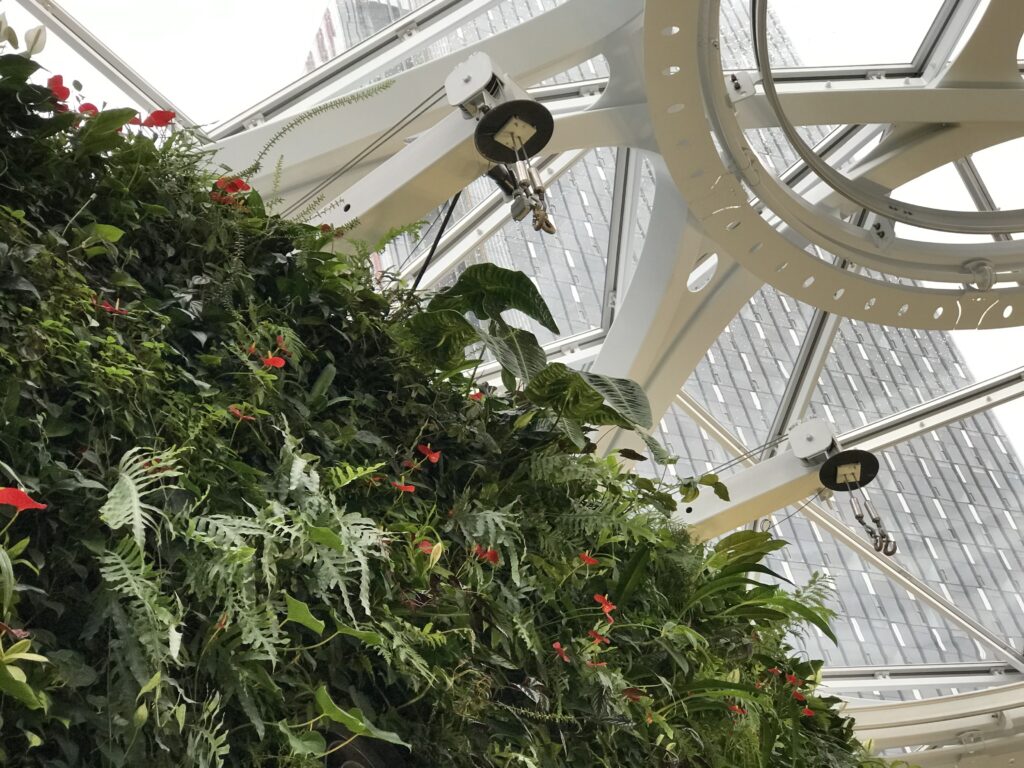
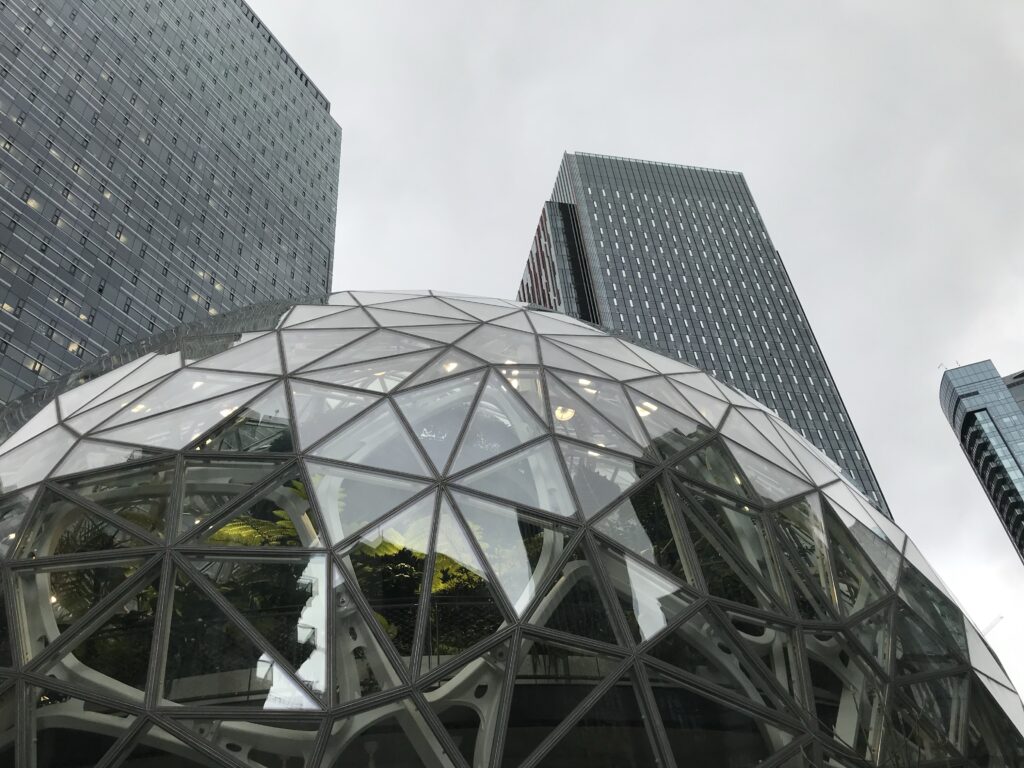
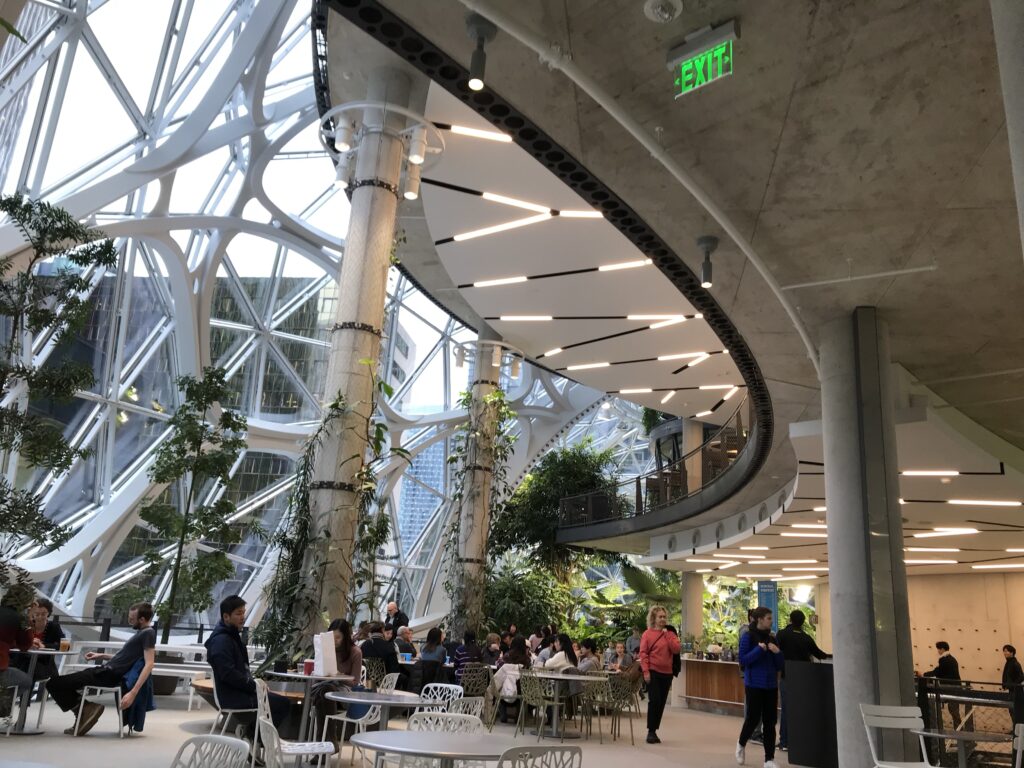













































The “Disneyland” Downtown Attraction Effect
The notion of downtown Seattle becoming a “Disneyland” attraction for remote workers represents an intriguing prospect. Several factors suggest both opportunities and limitations:
Supportive Elements:
- Light rail provides convenient, traffic-free access to downtown and sport arenas from throughout the regionyoutube
- Transit-oriented development near stations creates vibrant, walkable communities that could serve as intermediate destinationssoundtransit
- Survey data shows people who use transit report higher commute satisfaction than those who drive alonedowntownseattle

Limiting Factors:
- Despite infrastructure investments, downtown Seattle foot traffic remains only about 60% of pre-pandemic levels as of March 2025downtownseattle
- The substantial cost and complexity of the light rail system may not justify usage patterns dominated by occasional visits rather than regular commuting
- Competition from suburban office locations and distributed work arrangements reduces downtown’s monopoly as an employment center. However, Bellevue has a housing affordability problem whereas Seattle has made significant progress in that arena.
Seattle Center Rejection of Disney Proposal
Seattle Center is a 74-acre cultural and civic campus that originated as the site of the 1962 Seattle World’s Fair, envisioned to be a permanent hub for arts, science, and community gatherings. Anchored by the Space Needle and Climate Pledge Arena, it now hosts the Pacific Northwest Ballet, Seattle Opera, museums like MoPOP and the Pacific Science Center, and festivals such as Bumbershoot and the Seattle Center Festál series.
Its history stretches back to 1886, when David Denny donated the land for public use; major development began in the 1920s with the Civic Auditorium and Armory. In the late 1980s, consultants from Walt Disney Imagineering were hired to design a long-range redevelopment plan, which was ultimately rejected after public opposition over its high cost, commercialization, and proposed demolition of beloved historic landmarks.
Today, the Center thrives as Seattle’s cultural heart—offering ballet, opera, public art, food halls, and major events like the upcoming 2026 FIFA World Cup Fan Celebration.[1][2][4][11][12]
Sources
[1] Seattle Center – Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seattle_Center
[2] Seattle Center: After Century 21 – HistoryLink.org https://www.historylink.org/File/22588
[3] Seattle Center | SAH ARCHIPEDIA https://sah-archipedia.org/buildings/WA-01-033-0080
[4] History – Seattle Center https://www.seattlecenter.com/about/history
[5] [PDF] Historic Landmark study – Seattle Center https://www.seattlecenter.com/Documents/About/PlansAndProjects/LandmarkStudy_Seattle%20Center.pdf
[6] The History of the Seattle Center: A Timeline https://seattlemag.com/history-seattle-center-timeline/
[7] The City of Seattle and the 1962 World’s Fair – CityArchives https://www.seattle.gov/cityarchives/exhibits-and-education/online-exhibits/the-city-and-the-worlds-fair
[8] From Beatles to Sonics to Storm: Timeline of Seattle Coliseum and … https://www.seattletimes.com/sports/nba/from-beatles-to-sonics-to-storm-timeline-of-seattle-center-coliseum-and-keyarena/
[9] Brief History of Seattle – CityArchives https://www.seattle.gov/cityarchives/seattle-facts/brief-history-of-seattle
[10] Seattle Center Revealed: A Neighborhood History – YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=83NNT4rM324
[11] Disneyland in Seattle? Discover the Ambitious Plan that Would have … https://seattletravel.com/disneyland-in-seattle-discover-the-ambitious-plan-that-would-have-reshaped-downtown/
[12] Local Organizing Committee and Mayor Harrell Announce World … https://harrell.seattle.gov/2024/10/01/local-organizing-committee-and-mayor-harrell-announce-world-cup-fan-celebration-site-at-seattle-center/
Economic Reality:
While light rail undoubtedly makes downtown more accessible and attractive, the “Disneyland effect” faces practical constraints. The $20-30 billion budget shortfall for transit expansion suggests the system requires high-volume ridership rather than occasional visits from work at homers to justify its enormous public investment. The most successful transit-oriented developments combine residential density near stations with employment centers, creating consistent bidirectional travel patterns.
The future of Seattle’s light rail system will likely depend on achieving a balance between serving traditional commuter needs, supporting transit-oriented residential development, such as apartments rather than homes with offices, and adapting to evolving work patterns that blend remote and in-person employment. While light rail can certainly make downtown more accessible for occasional office visits, its long-term viability requires more substantial and consistent ridership than a pure “attraction” model would provide.
- https://www.constructiondive.com/news/seattle-sound-transit-light-rail-extensions-delayed-construction-problems/630689/
- https://komonews.com/news/local/sound-transit-west-seattle-light-rail-expansion-30-billion-construction-shortfall-increased-inflation-seattle-mayor-bruce-harrell-transportation-planner-rapid-bus-lines
- https://www.theurbanist.org/2025/10/02/op-ed-link-light-rails-success-depends-on-second-downtown-seattle-tunnel/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bertha_(tunnel_boring_machine)
- https://www.seattletimes.com/seattle-news/transportation/contractor-ordered-to-pay-state-over-tunnel-boring-machine-berthas-big-stall/
- https://www.courts.wa.gov/content/publicupload/eclips/2022%2009%2016%20Insurers%20dont%20have%20to%20pay%20for%20Highway%2099%20tunnel%20delays%20WA%20Supreme%20Court%20rules%20.pdf
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Downtown_Seattle_Transit_Tunnel
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/University_Link_tunnel
- https://www.soundtransit.org/blog/platform/8-facts-about-northgate-link-tunneling-project
- https://www.trainorders.com/discussion/read.php?4%2C6068762
- https://www.soundtransit.org/blog/platform/going-underground-east-link-light-rail-moving-forward-under-downtown-bellevue
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=405Jq_afPcs
- https://seattleelitetowncar.com/articles/fifa-world-cup-2026-seattle-guide/
- https://kingcounty.gov/en/dept/metro/programs-and-projects/transit-oriented-communities/northgate
- https://www.soundtransit.org/sites/default/files/documents/Transit-oriented%20Development%20Quarterly%20Report%20-%20Q4%202024.pdf
- https://www.seattletimes.com/seattle-news/transportation/roosevelt-light-rail-station-fuels-rapid-growth-in-north-seattle-neighborhood/
- https://downtownseattle.org/2025/05/seattle-magazine-seattle-commute-survey-shows-more-office-activity/
- https://kingcountymetro.blog/2025/04/28/survey-shows-transit-ridership-climbing-as-more-people-commute-to-downtown-seattle/
- https://www.claimsjournal.com/news/west/2021/08/05/305224.htm
- https://www.kiro7.com/news/local/insurers-claim-bertha-contractor-misled-on-true-cause-of-breakdown/596202887/
- https://www.theurbanist.org/2025/10/10/how-ballard-and-west-seattle-light-rail-became-a-30-billion-undertaking/
- https://harrell.seattle.gov/2025/09/02/mayor-harrell-proposes-actions-to-address-increased-sound-transit-expansion-costs-deliver-seattle-transit-expansion/
- https://www.trains.com/pro/passenger/light-rail/sound-transit-faces-30b-shortfall-what-it-means-for-seattle/
- https://seattletransitblog.com/2025/10/04/we-are-here-because-no-one-will-make-a-decision/
- https://www.soundtransit.org/system-expansion-progress-report
- https://www.reddit.com/r/Seattle/comments/1md9z77/jacobs_to_design_7b_seattle_light_rail_extension/
- https://acslawyers.com/damages/bertha-the-tunnel-is-finished-but-her-legacy-continues/
- https://www.soundtransit.org/ride-with-us/service-alerts
- https://www.soundtransit.org/blog/platform/link-reliability-improving-we-have-more-work-ahead
- https://www.reddit.com/r/Seattle/comments/1n2sy59/sound_transits_expansion_plans_balloon_by_up_to/
- https://www.soundtransit.org/blog/platform/update-link-projects-construction
- https://www.millernash.com/industry-news/seattle-tunnel-partners-bertha-case-sinks-as-appeal-hits-dead-end
- https://www.soundtransit.org/blog/platform/underground-seattle-transit-goes-rail-only-march-23
- https://www.soundtransit.org/blog/platform/digging-details-new-downtown-seattle-light-rail-tunnel
- https://www.soundtransit.org/blog/platform/looking-ahead-to-summers-big-soccer-tournament
- https://www.soundtransit.org/get-to-know-us/maps
- https://www.seattlechamber.com/world-cup/
- https://www.reddit.com/r/soundtransit/comments/1nggczi/part_2_alternative_downtown_tunnel_for_west/
- https://seattlefwc26.org/legacy/roadmap
- https://seattletransitblog.com/2025/02/28/ballard-light-rail-at-grade/
- https://www.reddit.com/r/Seattle/comments/y29f60/oc_sound_transit_complete_system_map_by_2044/
- https://www.soundtransit.org/get-to-know-us/news-events/news-releases/sound-transit-to-run-additional-service-club-world-cup
- https://www.soundtransit.org/blog/platform/9-quick-facts-about-how-u-link-was-built
- https://www.soundtransit.org/system-expansion/ballard-link-extension
- https://www.housingconsortium.org/housing-and-transit/
- https://www.soundtransit.org/sites/default/files/documents/Q1-2025-TOD-Quarterly-Report.pdf
- https://www.fox13seattle.com/news/seattle-commutes-home-jobs
- https://www.psrc.org/our-work/transit-oriented-development
- https://www.soundtransit.org/sites/default/files/documents/2025-Transit-Development-Plan.pdf
- https://www.soundtransit.org/system-expansion/creating-vibrant-stations/transit-oriented-development/projects
- https://www.reddit.com/r/Seattle/comments/yljxt7/will_having_a_light_rail_station_nearby_affect/
- https://downtownseattle.org/2025/04/commute-seattles-2024-survey-shifting-travel-patterns-citywide/
- https://www.reddit.com/r/transit/comments/1moj4rw/now_this_is_transit_oriented_development_redmond/
- https://seattle.gov/Documents/Departments/OPCD/OngoingInitiatives/NE130thAnd145thStationAreaPlanning/130th145thStationAreaPlanningFAQ.pdf
- https://www.commuteseattle.com/2024survey/
- https://www.soundtransit.org/system-expansion/creating-vibrant-stations/transit-oriented-development
- https://www.reddit.com/r/Seattle/comments/1nuevp1/as_fewer_in_seattle_work_remotely_heres_how/
- https://www.soundtransit.org/blog/platform/transit-oriented-development-opens-new-doors-seatac
- https://reasonstobecheerful.world/seattle-sound-transit-agency-affordable-housing/


