Seasickness is a condition caused by the confusion between different parts of the balance mechanism in the body. It occurs when the brain receives conflicting signals from the inner ear’s vestibular system, which senses motion and gravity, and other sensory inputs like vision. This sensory mismatch leads to symptoms such as nausea, headaches, dizziness, and fatigue3. Seasickness is a common issue for individuals on boats due to the conflicting signals received by the brain when the body registers motion but the eyes perceive stability.

As a yachtsman, I am a nautical landlubber.
On my father’s side I am descended from hardy New England stock. My forebears were the captains of windjammers, whalers which went out of Nantucket and remained for many months, clippers which raced to China and sailed the Seven Seas.
My dad always loved the water. The more it stormed, the better he liked it. He loved to feel a good stout deck quiver and shake beneath his feet as some heavy ocean roller shook the boat from stem to stern. At such times all the atavistic memories of prior incarnations of fearless sea captains would come to the front and he would stand braced against the wind, the salt spray hurtling past him, a look of keen enjoyment in his eyes.
My mother always got seasick. I take after my mother. Perhaps that is an oversimplification. My stomach takes after my mother.
Actually, I am a weird combination of mother and father. I love the water. I love adventure. I love the thrill of sailing to strange lands, of coming in to foreign ports…
Fortunately, very few people have really experienced seasickness. Nausea is, of course, a preliminary symptom, but it is no more indicative of seasickness than a chill and fever is indicative of malaria. It is what might be called an indispensable symptom, although I understand there are persons who claim to have become seasick without the nausea.
Erle Stanley Gardner

Differences from Car Sickness and Air Sickness:
- Car Sickness: Car sickness is similar to seasickness but occurs in a moving vehicle. It is also caused by conflicting sensory signals where the inner ear senses motion while the eyes perceive a stationary environment. Symptoms include nausea, dizziness, and fatigue.
- Air Sickness: Air sickness, experienced during flights, is also triggered by conflicting sensory inputs. The inner ear senses motion while visual cues may suggest stability. Symptoms include nausea, dizziness, and discomfort.
While the symptoms of motion sickness are consistent across different environments, such as boats, cars, and airplanes, seasickness specifically relates to the experience of motion sickness on watercraft due to the unique conditions and movements encountered at sea3.
Here is a discussion on how water ballast, gyroscopes, tabs, sails, sea anchors, keels, and course can help avoid seasickness:

Yacht World reports that Sailing ships as early as the 17th century used to hold water (in barrels) all secured in place, in the lower part of their hulls for its sea kindly features.
- Water Ballast: Water ballast can add stiffness to a boat, enhancing stability without significantly increasing weight. By adjusting the amount of water ballast, sailors can control a vessel’s displacement, providing comfort in rough seas while maintaining efficiency in light airs5.
- Gyroscopes (Gyro Stabilizers): Gyro stabilizers can significantly reduce boat roll, helping prevent seasickness by providing a more stable platform. They act as underwater wings that reduce the boat’s lateral rocking motion3.
- Tabs (Trim Tabs): Trim tabs are adjustable surfaces on the hull that help control the boat’s attitude and stability. Properly adjusted trim tabs can improve the boat’s ride in rough seas and reduce motion that may lead to seasickness2.
- Interceptors: Trim tabs comprise flat plates, arranged symmetrically port and starboard, that hinge along the front edge. Pushing either or both plates down into the water that flows aft from the transom creates a pressure build-up that pushes the plates, and hence the stern, upwards.
Interceptors generate the same pressure build-up, but use a flat blade that descends vertically into the water flow. That immersion generates a wedge of inert water in front of the blade, and that wedge mimics the effect of a conventional downward-angled trim tab plate.4 - Sails: Sailing can provide a smoother ride compared to motorized boats, potentially reducing the likelihood of seasickness. The natural movements of sailing in harmony with the wind and waves can be less likely to induce motion sickness2.
- Sea Anchors: Sea anchors can be deployed to stabilize a boat in rough seas by reducing drift and controlling its orientation to the waves, potentially minimizing motion that contributes to seasickness.
- Keels: Keels play a role in stabilizing a boat by providing lateral resistance and preventing excessive rolling. Well-designed keels contribute to the overall stability of the vessel, reducing motion that may cause seasickness.
- Course Adjustments: Changing course to navigate in calmer waters or aligning the boat with the waves can help reduce discomfort and motion sickness symptoms5.

Water Ballast
Water ballast in boats offers several benefits, including improved stability and performance. Water ballast can add stiffness to a boat, enhancing its stability without significantly increasing weight1. By adjusting the amount of water ballast, sailors can control a vessel’s displacement, providing comfort in rough seas while maintaining efficiency in light airs1.
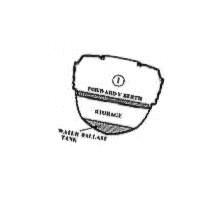
Water ballast can also contribute to a boat’s righting moment, making it sail more upright and efficiently, resulting in less hull drag, reduced weight on the helm, and improved sail performance1. Additionally, water ballast tanks are crucial for ship safety and structural integrity. Overall, water ballast can enhance a boat’s stability, performance, and safety, making it a valuable feature for sailors seeking comfort and efficiency on the water.
Gyroscopes
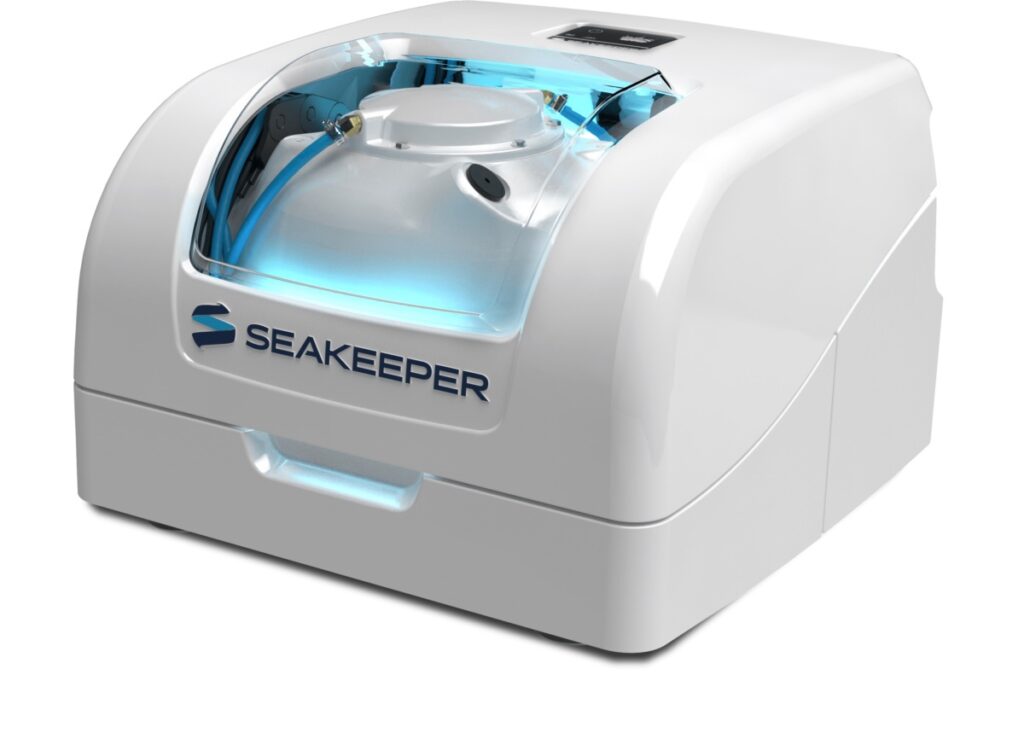

SeaKeeper offers gyro stabilizers that help prevent seasickness by significantly reducing boat roll, which is a major cause of seasickness. These state-of-the-art stabilizers are designed to counteract the side-to-side rocking motion induced by choppy waters, effectively eliminating up to 95% of boat roll2. By utilizing a rotor moving around an axis, the gyro stabilizer generates a powerful gyroscopic torque that stabilizes the boat even in challenging conditions2.

The low energy consumption of Seakeeper gyro stabilizers, using only about half the power of an average air conditioner, makes them efficient and practical for boats2. Users have reported experiencing reduced fatigue, anxiety, and nausea associated with seasickness, making boating a more pleasant and comfortable experience whether trolling, cruising, or at anchor2. Overall, Seakeeper gyro stabilizers offer a solution to seasickness by providing enhanced stability and reducing the disruptive effects of boat roll.
Tabs (Trim Tabs)
A stabilizer on a boat is an addition that helps stabilize the vessel and reduce rocking, particularly in rough seas. Stabilizers act as underwater wings, decreasing the boat’s tendency to rock laterally2. They are commonly found on larger motor yachts and superyachts, enhancing comfort for passengers by minimizing the boat’s motion2.
Stabilizers play a crucial role in preventing seasickness by reducing the boat’s rocking motion, which is a significant factor contributing to motion sickness. By stabilizing the boat, these systems help maintain a more stable platform, reducing the likelihood of passengers experiencing seasickness symptoms2. Larger boats often have stabilizers to help keep them steady in rough seas, making them a preferred choice for those prone to seasickness2.
Sails
Sails can help prevent seasickness by providing a smoother ride compared to motorized boats. When sailing, the boat moves in harmony with the wind and waves, resulting in a more natural and gentle motion that can be less likely to induce seasickness2. Additionally, sailing allows passengers to feel the wind and experience the elements, which can help reduce feelings of nausea and discomfort associated with seasickness2.

Furthermore, sailing involves more natural movements that are in sync with the environment, potentially reducing the sensory conflicts that contribute to seasickness3. While sailing may not completely eliminate the risk of seasickness for everyone, it can offer a more enjoyable and comfortable experience on the water for those prone to motion sickness.
Sea Anchors
Drogues, which are devices deployed in the water to create drag and stabilize a boat, can help prevent seasickness by reducing the rolling motion of the vessel. By slowing down the boat’s movement through the water, drogues can dampen the effects of waves and reduce the boat’s tendency to roll excessively, potentially alleviating seasickness symptoms for those on board5.
While drogues can be effective in stabilizing a boat and minimizing motion sickness, it is essential to consider individual preferences and sensitivities when choosing methods to prevent seasickness. Other strategies such as staying hydrated, focusing on the horizon, avoiding strong odors, and maintaining a calm demeanor can also contribute to reducing seasickness symptoms while out on the water4.
Keels
Keels on boats play a crucial role in preventing seasickness by contributing to the vessel’s stability. Keels provide lateral resistance, helping to counteract the rolling motion induced by waves and reducing the boat’s tendency to rock excessively3. By stabilizing the boat and minimizing excessive rolling, keels can help create a smoother and more comfortable ride for passengers, potentially reducing the likelihood of seasickness.

In combination with other factors such as boat size, design, and sailing conditions, keels contribute to enhancing the overall stability of the vessel, making it less susceptible to the motions that can trigger seasickness3. Therefore, choosing a boat with a well-designed keel can be beneficial in minimizing the effects of seasickness while underway.

Course Adjustments
Changing course can sometimes help prevent seasickness by altering the boat’s motion and reducing the effects of waves on passengers. By adjusting the boat’s direction, the captain can potentially find a more stable heading that minimizes the rolling or pitching motion that contributes to seasickness5. Changing course to navigate in calmer waters or to align the boat with the waves can help reduce the discomfort experienced by passengers prone to motion sickness5.

While changing course may offer temporary relief from seasickness, it is essential to consider individual preferences and sensitivities when managing symptoms. Combining course adjustments with other strategies like staying hydrated, focusing on the horizon, and avoiding strong odors can further help alleviate seasickness while at sea4.
To avoid seasickness while underway and when drifting or at anchor, the following considerations can be helpful based on the information provided in the search results:

- Boat Size: Larger boats are generally more stable and less prone to rocking, making them better for avoiding seasickness12.
- Stability (Width): The width of the boat, known as the beam, influences how it behaves in the water. Wider beams typically result in less rocking back and forth1.
- Catamarans: Catamarans are known for their stability due to their design with two hulls, making them a good choice to minimize seasickness12.
- Gyro Stabilizers: Gyro stabilizers can significantly reduce boat roll, helping prevent seasickness by providing a more stable platform5.
- Course Adjustments: Changing course to navigate in calmer waters or aligning the boat with the waves can help reduce discomfort and motion sickness symptoms5.
- Visibility: Focusing on the horizon can provide a reference point for the brain, aiding in reducing seasickness symptoms2.
- Medications: Seasickness medications like scopolamine patches or meclizine can be taken to alleviate symptoms5.
- “Some sailors have had success using a bracelet with an acupressure button applied to the wrist. A Reliefband generates a pulse through the soft side of the wrist in a way that the manufacturer says normalizes nerve messages from the brain to the stomach. Another company that produces a wristband is EmeTerm.”
By considering these factors and utilizing strategies like choosing a stable boat, using stabilizing technologies, adjusting course, and taking medications if needed, individuals can enhance their comfort and reduce the likelihood of experiencing seasickness while on the water.
To avoid seasickness while underway or at anchor, larger and more stable boats like catamarans or large ships are recommended1.

Catamarans are known for their stability due to their wide beam, making them less prone to rocking back and forth in the water1.

Additionally, boats with stabilizers, such as some cruise ships or motor yachts, can help reduce motion in rough seas15. When choosing a boat to minimize seasickness, factors like size (length), beam (width), and visibility play crucial roles1. The wider the beam of a boat, the less it will typically rock in the water1.

For those prone to seasickness, staying in the center of the boat and low, avoiding front berths, reducing alcohol and caffeine consumption, sleeping on your back, avoiding greasy foods, and keeping busy can help alleviate symptoms5.

Some medications can also be taken to reduce seasickness effects5. Ultimately, selecting a boat with features like stabilizers or opting for a catamaran or a water ballasted boat can significantly improve comfort and reduce the likelihood of seasickness.

The various ways to avoid seasickness discussed in the provided sources include:
- Maintaining Normal Routines: Eating, drinking, and resting as you would at home can help prevent seasickness1.
- Ginger: Consuming ginger in various forms like raw, candied, or brewed in tea can help settle the stomach and reduce seasickness symptoms2.
- Looking at the Horizon: Focusing on the horizon can provide a point of reference for the brain, helping to alleviate motion sickness by resolving conflicting sensory signals2.
- Sea Bands: These elastic bracelets with a plastic stud that applies pressure to an acupressure point are believed to relieve nausea and vomiting, although scientific evidence on their effectiveness is mixed2.
- Medication: Various seasickness medications like scopolamine patches, meclizine, diphenhydramine, and other prescription drugs can help soothe symptoms of seasickness5.
- Fresh Air: Getting fresh air, particularly at higher points on the boat, can help reduce nausea and clear the head3. The small battery powered fans are effective below decks.
- Rest: Ensuring you are well-rested before your cruise can minimize the effects of seasickness3. Taking frequent short naps can reset the mechanisms causing sea sickness.
- Light and Healthy Foods: Eating light and healthy foods can help avoid aggravating seasickness symptoms3. Frequent snacking is also valuable.
- Avoiding Alcohol: Alcohol can intensify seasickness, so it’s best to avoid it while on a boat3. So does caffeinated beverages.
- Sitting Towards the Middle of the Boat: Sitting towards the middle of the boat can help lessen motion sickness effects by reducing movement extremes3. The lowest middle portion of any vessel will the position that is stable, with increased motion as you move forward or aft and to the port or starboard.
“By incorporating these strategies into your sailing experience, you can increase your chances of preventing or minimizing seasickness and enjoy a smoother ride on the water.
Once upon a time, Jack, a skilled operator of a Macgregor 26x, planned a sailing date with Jill, hoping to impress her with his sailing prowess and the beauty of the sea.

The Macgregor 26x, known for its versatility as both a sailboat and powerboat, was the perfect vessel for their adventure.
As they set sail, Jack was mindful of the potential for seasickness, especially since Jill was new to sailing. He decided to use the sails to provide a smoother ride, harnessing the wind’s power to glide gracefully over the waves. The natural and steady motion of sailing, he hoped, would be less likely to induce seasickness compared to the more abrupt movements of motoring.

To further ensure Jill’s comfort, Jack adjusted the water ballast, adding stability to the boat by increasing its weight and lowering its center of gravity.
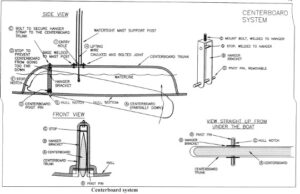
This, combined with the strategic positioning of the swing keel, optimized the boat’s balance and minimized the rolling motion that often leads to seasickness.
As they enjoyed the sail, a squall appeared on the horizon. Jack knew he had to act quickly to maintain the serenity of their journey. He made course changes to avoid the worst of the weather and smooth the ride seeking quieter waters. Despite the changing conditions, Jill stayed on deck, assisting with navigation. Her cheerful demeanor and willingness to be a good sport made the experience even more enjoyable for both of them.

Eventually, Jack decided it was best to motor to a somewhat protected cove where he deployed a sea anchor, ensuring their stability as the squall passed.
At one time, on the Alaskan trip, it became necessary to anchor the boat in a small cove and put me ashore for twenty-four hours. I had become so nauseated that in between spells of retching my body muscles would be seized with cramps which would tie them in knots. Running a hand over my body, my torso felt like a sack of potatoes. The pain, of course, was excruciating.
I have an idea I would have died if I hadn’t been put ashore to recuperate.
Erle Stanley Gardner

Jill’s assistance and positive attitude throughout the ordeal only deepened Jack’s admiration for her.
After the squall, Jack utilized the Macgregor 26x’s ability to motor fast back to the harbor, ensuring they made their dinner reservations.

During dinner, Jill revealed she had taken seasickness pills as a precaution, a detail she hadn’t shared with Jack earlier.
They laughed about their adventure and the secrets they had kept to ensure a smooth sailing experience.
Years later, Jack and Jill often reminisced about that day as they celebrated their 25th wedding anniversary. The Macgregor 26x, still part of their lives, served as a testament to their enduring love and shared adventures. Their story became a cherished tale of how a skilled sailor, a versatile boat, and a willing partner turned a potentially challenging day at sea into the beginning of a lifelong journey together.
Anyone who is a good sailor, fortunate enough to live along the West Coast of the United States, will find that dollar-for-dollar money invested in a yacht will give him more relaxation, more thoroughgoing enjoyment, more health, more peace of mind than any similar investment he can make.
Erle Stanley Gardner
Erle Stanley Gardner (1889-1970) was a prolific American author and lawyer, best known for creating the iconic fictional lawyer-detective Perry Mason. However, his importance to boaters stems from his passion for maritime adventures and his writings about his experiences on the water.
Gardner’s Maritime Connection
Gardner was a seasoned yachtsman with a complex relationship with sailing. Despite suffering from severe seasickness, which he humorously described himself as an expert in, his adventurous spirit drove him to embark on numerous nautical journeys1. He sailed to various destinations, including Hong Kong, Manila, Alaska, and the Baja California peninsula1.
Books for Boaters
In his later years, Gardner focused on more peaceful ventures along the Sacramento Delta, which inspired him to write three books about his experiences:
- “The World of Water”
- “Gypsy Days on the Delta”
- “Drifting down the Delta”
These books are not traditional travel guides or adventure stories, but rather journal-like accounts of Gardner’s leisurely explorations of the Delta’s inland waterways1.They offer readers a glimpse into the early history of the area, including the era when riverboats were the primary means of commerce between San Francisco, Stockton, and Sacramento1.
Importance for Boaters
Gardner’s Delta books are significant for boaters for several reasons:
- Historical perspective: They provide insights into the maritime history of the Sacramento Delta region.
- Personal experiences: Readers can learn from Gardner’s firsthand accounts of navigating the waterways.
- Local knowledge: The books offer information about local establishments, such as Giusti’s Place, which Gardner frequently mentioned as his favorite Delta hangout1.
- Visual documentation: The books contain numerous personal photographs of friends, watercraft, and scenery from the Delta’s past1.
Other Notable Works
While his boating-related books are of particular interest to maritime enthusiasts, Gardner was primarily known for his prolific output of mystery novels. Some of his most famous works include:
- The Perry Mason series (85 novels)
- The Donald Lam-Bertha Cool mystery series (published under the pseudonym A. A. Fair)
- Various pulp fiction stories and novellas
By the time of his death, Gardner had become one of the most widely read American authors, with his books selling millions of copies worldwide25. His Perry Mason novels, in particular, were incredibly popular, selling at a rate of 20,000 copies per day in the mid-1950s2.In addition to his fiction, Gardner also wrote nonfiction books about his travels through Baja California and other regions in Mexico, further demonstrating his love for exploration and adventure5.
Sea Anxiety
Sea anxiety and seasickness are closely related conditions that can affect individuals when traveling on water. While they are distinct, they often interact and exacerbate each other.
Sea Anxiety
Sea anxiety, also known as thalassophobia, is a fear or apprehension related to sea travel or being on the water. This condition can manifest in various ways:
- Intense worry or dread about potential seasickness
- Fear of the open water or deep sea
- Anxiety about potential dangers at sea
- Nervousness about being far from land
Sea anxiety can occur before or during a sea journey and may be triggered by past negative experiences or simply the anticipation of discomfort.
Relationship to Seasickness
The relationship between sea anxiety and seasickness is complex and often bidirectional:
- Anxiety as a Precursor: Anxiety about getting seasick can actually increase the likelihood of experiencing seasickness. The stress and tension associated with this fear can make an individual more susceptible to motion sickness5.
- Exacerbation of Symptoms: Anxiety can worsen the symptoms of seasickness. When an individual is anxious, they may be more attuned to physical sensations, amplifying feelings of nausea or dizziness5.
- Feedback Loop: As seasickness symptoms develop, anxiety may increase, creating a cycle that intensifies both conditions5.
- Anticipatory Anxiety: Fear of seasickness can lead to anticipatory anxiety, causing stress even before embarking on a sea journey8.
- Impact on Adaptation: Research suggests that psychological factors, including anxiety and depression, may affect an individual’s ability to adapt to seasickness over time7.
Managing Sea Anxiety and Seasickness
Addressing both sea anxiety and seasickness often requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Relaxation Techniques: Using relaxation methods can help reduce anxiety, which may, in turn, alleviate seasickness symptoms6.
- Medication: Anti-motion sickness medications can help with physical symptoms, potentially reducing anxiety about getting sick.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: For severe cases of sea anxiety, professional counseling may be beneficial6.
- Gradual Exposure: Building positive experiences on the water can help reduce anxiety over time.
- Education: Understanding the causes of seasickness and learning coping strategies can help alleviate fears and anxiety.
Children aged 2-12 years are generally more susceptible to motion sickness, with peak susceptibility occurring around ages 9-10. Specifically:
- Children under 2 years old are typically resistant to motion sickness.
- Susceptibility increases in childhood, peaking between ages 9-12.
- Teenagers and adults over 50 are less likely to experience motion sickness.
Regarding ethnic differences in susceptibility to motion sickness:
- Some studies suggest that individuals of Asian ancestry may be more prone to motion sickness compared to those of European ancestry.
- However, research findings are mixed, with some studies showing conflicting results.
- A study in Germany found that Asian participants reported less motion sickness than White participants, but had shorter rotation tolerance.
It’s important to note that these ethnic differences may reflect cultural and social factors rather than biological ones, as race is considered a social construct rather than a genetic one. Factors such as reporting differences, cultural conditioning, and attention to uncomfortable stimuli may play a role in observed ethnic variations in motion sickness susceptibility.
Pregnant women and menstruating women are generally more susceptible to seasickness compared to others. Pregnant women experience increased susceptibility to motion sickness due to hormonal changes, particularly elevated estrogen levels. These hormonal shifts affect the inner ear, a key component of the body’s balance system, leading to heightened sensitivity to motion stimuli.
For menstruating women, susceptibility to motion sickness fluctuates throughout the menstrual cycle. Studies have shown that women tend to be more susceptible to motion sickness during the peri-menses phase (around menstruation) compared to the peri-ovulatory phase. Women not using oral contraceptives reported more severe symptoms of nausea and motion sickness during the peri-menses phase when exposed to motion stimuli.
By addressing both the psychological (anxiety) and physiological (seasickness) aspects, individuals can often improve their overall experience on the water and reduce the impact of both conditions.
1. Feelings vs facts
Often, people tend to believe what they feel. They forget that the negative thoughts are just a thought and not true.
For example, feelings like the boat will sink, are just a thought and are likely not true. This is especially the case for boats like Etaps, Boston Whalers and Macgregor 26 vessels that have positive flotation.
2. Possibilities over likeliness
Coming again with a difference of realism, there are many possibilities but not all that are likely to happen. people can think of many things that could go wrong.
For instance, starting a fire while cooking, losing an important boat fitting, getting hit by a car ferry, losing an item overboard, clogging the head, even destroying a marriage/ friendship/ relationship represent a wide range of possibilities on boats
3. Devious trenches of mind-reading
To make an impression, we tend to figure out what the other person may be thinking. While thinking about it may be fine, we don’t realize when our thinking turns into an assumption.
You may think that people on the boat are judging you for your attire and boating capabilities but it is important to stop and ask yourself, “Am I mind-reading?”
4. Overgeneralizing
It often takes one person to hurt us for us to believe that no one in general should be trusted. We make broad conclusions from a single negative encounter that pushes us to think in a biased direction.
When you find yourself diving into negativities of a situation, ask yourself, “Am I overgeneralizing?”
5. “What am I doing right?”
We are quick to ask, “What went wrong?” or “What did I do wrong?” but how about turning the question around instead?
Ask yourself, “What am I doing right?” when you feel like you’re sinking into negative introspection. For some captains just being aware of or asking when you need to move is doing it right. Just not falling into the water is significant. It is always right to wear a life jacket because it encourages others to do so. It’s a matter of perception and realization—don’t let negativity blind you.
Ginger and Pepperment
Both ginger and peppermint can help prevent seasickness:
Ginger:
• Reduces nausea and vomiting associated with motion sickness
• As effective as dimenhydrinate (Dramamine) with fewer side effects
• Can be taken as capsules (1 gram) one hour before travel and every 2-4 hours as needed
Peppermint:
• Helps relieve nausea symptoms of motion sickness
• Can be consumed as tea or tablets
• Peppermint oil can be applied to temples or inhaled for aromatherapy benefits
Both can be consumed as teas or in other forms:
• Ginger tea or ginger cookies may provide mild relief
• Peppermint-infused teas are effective for upset stomach and nausea
While these natural remedies can be helpful, their effectiveness may vary among individuals. For severe cases, prescription medications might be more suitable.
Ear plug
Using one earplug can help prevent seasickness, but the effectiveness may vary and there’s conflicting information about which ear to use:
1. Some sources suggest using an earplug in the non-dominant ear (left for right-handed people, right for left-handed).
2. Others claim the ear choice doesn’t matter, as long as only one ear is plugged.
3. The method works by disrupting conflicting sensory signals to the brain, potentially reducing motion sickness symptoms.
4. Effectiveness can vary, with some reporting significant relief within minutes, while others may not experience the same benefits.
5. This method is drug-free and can be used for various forms of motion sickness, including car, air, and sea travel.
While promising, more research is needed to fully understand and validate this approach. It’s a simple, low-risk method worth trying for those suffering from seasickness.
Naps
Quick naps can help prevent seasickness. Sleeping it off is mentioned as one of the best ways to tackle seasickness1. Napping in the center cabin, where movement is often weakest, can be beneficial3.Fans and ventilation are also effective in preventing seasickness:
- Blowing air on your face can help prevent motion sickness2. Many theme parks and rides use fans to combat nausea.
- Fresh air circulation is recommended. Opening windows or using a fan can help reduce seasickness symptoms6.
- A fan provides a sense of direction and anchors you to the real world, which can help with motion sickness9.
- Having a breeze of fresh air and avoiding enclosed spaces can help with seasickness10.
Using fans or ensuring good ventilation is a simple yet effective method to reduce the likelihood of experiencing seasickness during your trip26910.
UNDERSTANDING SEASICKNESS
Prevention
1. Pre-Departure Tips
• Diet and hydration recommendations.
• Adequate rest before sailing.
• Choosing the right location on the boat for stability.
2. Behavioral Techniques
• Keeping your eyes on the horizon.
Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms (reading, screen time).
Gradual exposure for newcomers.
3. Boat Setup and Environmental Adjustments
Ventilation and fresh air.
Stabilizing the boat when possible.
Signs and Symptoms
Early: extreme drowsiness, headache, fatigue
Yawning, sighing, cold and clammy skin, dry mouth, lethargy
Nausea following by vomiting
Rapid deterioration of mental, physical, and emotional function manifests in poor judgement, lapses in memory, irritability, loss of manual dexterity and poor balance.
Treatment Options
1. Over-the-Counter Medications
• Types (e.g., meclizine, dimenhydrinate, scopolamine patches).
2. Home Remedies
Ginger, peppermint, and other natural approaches.
Acupressure bands and other non-pharmaceutical aids.
One Ear Plug
3. Advanced Medical Interventions
• Prescription options for severe cases- Phenergen,
Recognizing when professional medical attention is needed.
Managing Seasickness
- 1. Focus on the horizon to help align visual input with motion sensations.
- 2. Stand on deck and try to maintain balance, which helps your nervous system adapt to the ship’s motion.
- 3. Stay active and distract yourself with activities like walking on deck or exercising.
- 4. Use medication such as Dramamine or Bonine, starting 1-2 days before boarding.
- 5. Try acupressure wristbands.
- 6. Apply a scopolamine patch behind the ear.
- 7. Practice proper breathing techniques to ease nausea.
- 8. Stay hydrated, but avoid acidic drinks, caffeine, and alcohol.
Remember, seasickness typically improves within 48 hours for most passengers as they acclimate to the ship’s motion.


